Paging in Operating System
Paging is a memory management scheme that eliminates the need for a contiguous allocation of physical memory. The process of retrieving processes in the form of pages from the secondary storage into the main memory is known as paging . The basic purpose of paging is to separate each procedure into pages. Additionally, frames will be used to split the main memory. This scheme permits the physical address space of a process to be non – contiguous.
In paging, the physical memory is divided into fixed-size blocks called page frames , which are the same size as the pages used by the process. The process’s logical address space is also divided into fixed-size blocks called pages, which are the same size as the page frames. When a process requests memory, the operating system allocates one or more page frames to the process and maps the process’s logical pages to the physical page frames.
The mapping between logical pages and physical page frames is maintained by the page table, which is used by the memory management unit to translate logical addresses into physical addresses. The page table maps each logical page number to a physical page frame number.
Terminologies Associated with Memory Control
- Logical Address or Virtual Address: This is a deal that is generated through the CPU and used by a technique to get the right of entry to reminiscence. It is known as a logical or digital deal because it isn’t always a physical vicinity in memory but an opportunity for a connection with a place inside the device’s logical address location.
- Logical Address Space or Virtual Address Space: This is the set of all logical addresses generated via a software program. It is normally represented in phrases or bytes and is split into regular-duration pages in a paging scheme.
- Physical Address: This is a cope that corresponds to a bodily place in reminiscence. It is the actual cope with this that is available on the memory unit and is used by the memory controller to get admission to the reminiscence.
- Physical Address Space: This is the set of all bodily addresses that correspond to the logical addresses inside the way’s logical deal with place. It is usually represented in words or bytes and is cut up into fixed-size frames in a paging scheme.
In a paging scheme, the logical deal with the region is cut up into steady-duration pages, and every internet web page is mapped to a corresponding body within the physical deal with the vicinity. The going for walks tool keeps a web internet web page desk for every method, which maps the system’s logical addresses to its corresponding bodily addresses. When a method accesses memory, the CPU generates a logical address, that is translated to a bodily address using the net page table. The reminiscence controller then uses the physical cope to get the right of entry to the reminiscence.
Important Features of Paging in PC Reminiscence Management
- Logical to bodily address mapping: In paging, the logical address area of a technique is divided into constant-sized pages, and each web page is mapped to a corresponding physical body within the main reminiscence. This permits the working gadget to manipulate the memory in an extra flexible way, as it is able to allocate and deallocate frames as needed.
- Fixed web page and frame length: Paging makes use of a set web page length, which is usually identical to the size of a frame within the most important memory. This facilitates simplifying the reminiscence control technique and improves device performance.
- Page desk entries: Each page within the logical address area of a method is represented through a page table entry (PTE) , which contains facts approximately the corresponding bodily body in the predominant memory. This consists of the frame range, in addition to other manipulate bits which can be used by the running machine to manage the reminiscence.
- A number of page desk entries: The range of page desk entries in a manner’s page desk is identical to the wide variety of pages inside the logical deal with the area of the technique.
- Page table stored in important memory: The web page desk for each system is typically saved in important reminiscence, to allow for green get right of entry to and change by the operating device. However, this could additionally introduce overhead, because the web page table must be updated on every occasion a system is swapped in or out of the main memory.
How Paging Works?
Paging is a method used by operating systems to manage memory efficiently. It breaks physical memory into fixed-size blocks called “frames” and logical memory into blocks of the same size called “pages.” When a program runs, its pages are loaded into any available frames in the physical memory.
This approach prevents fragmentation issues by keeping memory allocation uniform. Each program has a page table, which the operating system uses to keep track of where each page is stored in physical memory. When a program accesses data, the system uses this table to convert the program’s address into a physical memory address.
Paging allows for better memory use and makes it easier to manage. It also supports virtual memory, letting parts of programs be stored on disk and loaded into memory only when needed. This way, even large programs can run without fitting entirely into main memory.
- If Logical Address = 31 bit, then Logical Address Space = 2 31 words = 2 G words (1 G = 2 30 )
- If Logical Address Space = 128 M words = 2 7 * 2 20 words, then Logical Address = log 2 2 27 = 27 bits
- If Physical Address = 22 bit, then Physical Address Space = 2 22 words = 4 M words (1 M = 2 20 )
- If Physical Address Space = 16 M words = 2 4 * 2 20 words, then Physical Address = log 2 2 24 = 24 bits
The mapping from virtual to physical address is done by the Memory Management Unit (MMU) which is a hardware device and this mapping is known as the paging technique.
- The Physical Address Space is conceptually divided into a number of fixed-size blocks, called frames .
- The Logical Address Space is also split into fixed-size blocks, called pages .
- Page Size = Frame Size
Example
- Physical Address = 12 bits, then Physical Address Space = 4 K words
- Logical Address = 13 bits, then Logical Address Space = 8 K words
- Page size = frame size = 1 K words (assumption)
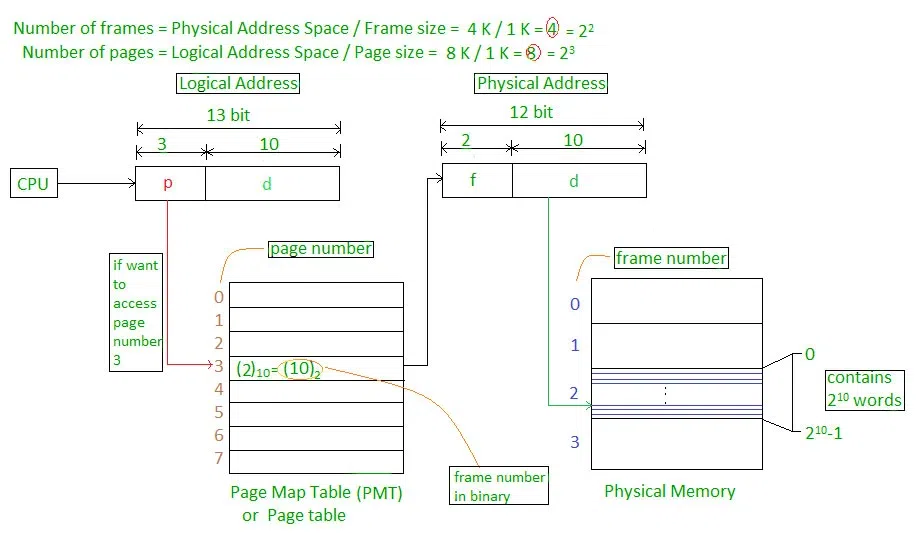
The address generated by the CPU is divided into
- Page number(p): Number of bits required to represent the pages in Logical Address Space or Page number
- Page offset(d): Number of bits required to represent a particular word in a page or page size of Logical Address Space or word number of a page or page offset.
In a paging scheme, the physical cope with the area is divided into fixed-length frames, each of which contains some bytes or words. When a manner is running, its logical address space is split into constant-size pages, which might be mapped to corresponding frames within the physical address space.
Physical Address is divided into:
To represent a physical address in this scheme, parts are commonly used:
Frame Range: This is the variety of the frame within the physical cope with the area that consists of the byte or phrase being addressed. The wide variety of bits required to represent the body range relies upon the scale of the physical cope with the area and the size of each frame. For instance, if the physical cope with area carries 2^20 frames and each frame is 4KB (2^12 bytes) in size, then the frame range could require 20-12 = 8 bits.
Frame Offset: This is the wide variety of the byte or word within the body this is being addressed. The number of bits required to represent the frame offset relies upon the size of every frame. For instance, if everybody is 4KB in size, then the frame offset could require 12 bits. So, a physical address in this scheme may be represented as follows:
- The TLB is associative, high-speed memory.
- Each entry in TLB consists of two parts: a tag and a value.
- When this memory is used, then an item is compared with all tags simultaneously. If the item is found, then the corresponding value is returned.
Paging is a memory management technique used in operating systems to manage memory and allocate memory to processes. In paging, memory is divided into fixed-size blocks called pages, and processes are allocated memory in terms of these pages. Each page is of the same size, and the size is typically a power of 2, such as 4KB or 8 KB.
Important Points About Paging in Operating Systems
- Reduces internal fragmentation: Paging facilitates lessening internal fragmentation by using allocating memory in fixed-size blocks (pages), which might be usually a whole lot smaller than the size of the process’s facts segments. This lets in for greater efficient use of memory in view that there are fewer unused bytes in each block.
- Enables reminiscence to be allotted on call for: Paging enables memory to be allocated on call for, this means that memory is most effectively allocated when it’s far needed. This allows for extra efficient use of memory in view that only the pages that are absolutely used by the manner want to be allocated inside the physical memory.
- Protection and sharing of memory: Paging allows for the protection and sharing of reminiscence between methods, as each procedure has its own web page table that maps its logical deal with area to its physical address space. This permits techniques to proportion facts at the same time as preventing unauthorized get right of entry to every other’s memory.
- External fragmentation: Paging can result in outside fragmentation, wherein memory turns fragmented into small, non-contiguous blocks. This can make it difficult to allocate massive blocks of reminiscence to a method seeing that there may not be enough contiguous free memory to be had.
- Overhead: Paging involves overhead because of the renovation of the web page table and the translation of logical addresses to physical addresses. The working device must maintain the page table for each manner and perform a deal with translation whenever a procedure accesses memory, which can slow down the machine.
What is Memory Management Unit (MMU)?
A memory management unit (MMU) is a technique used to convert logical address to physical address. Logical address is the address generated by CPU for each page and physical address is the real address of the frame where page is going to be stored.
Whenever a page has to be accessed by CPU using the logical address, it requires physical address for accessing the page. Logical address comprises of two parts: Page Number and Offset.
Conclusion
In conclusion, paging is a memory management technique that helps computers in storing data efficiently and it also helps in retrieve data as it breaks the memory into small, fixed size chunks called pages. It helps in handling larger amount of data without the issue of fragmentation that improves the performance and usability.
Frequently Asked Questions on Paging – FAQs
What is the use of Paging in an Operating System?
Paging is a memory management technique that is used to retrieve processes from secondary storage to main memory.
What is the basic advantage of Paging?
Paging reduces internal fragmentation and in paging there is a possibility of external fragmentation.
What is the effect of Paging?
Paging helps in improving the performance of the system by improving the utilization of the memory and accessing the available memory present there.


